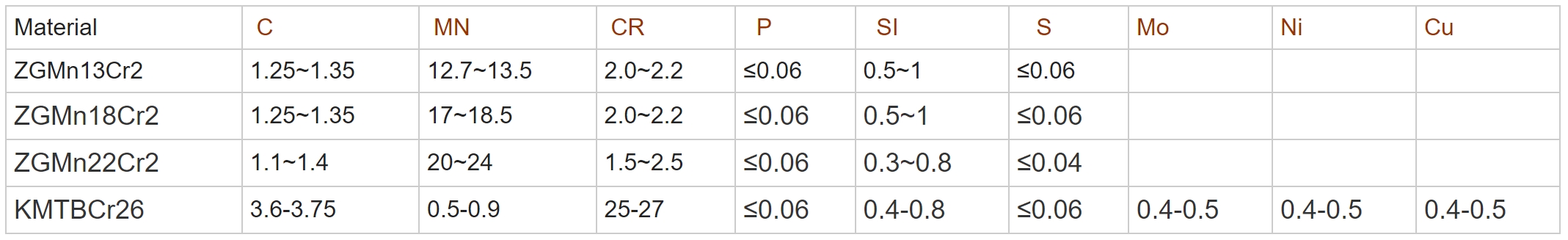
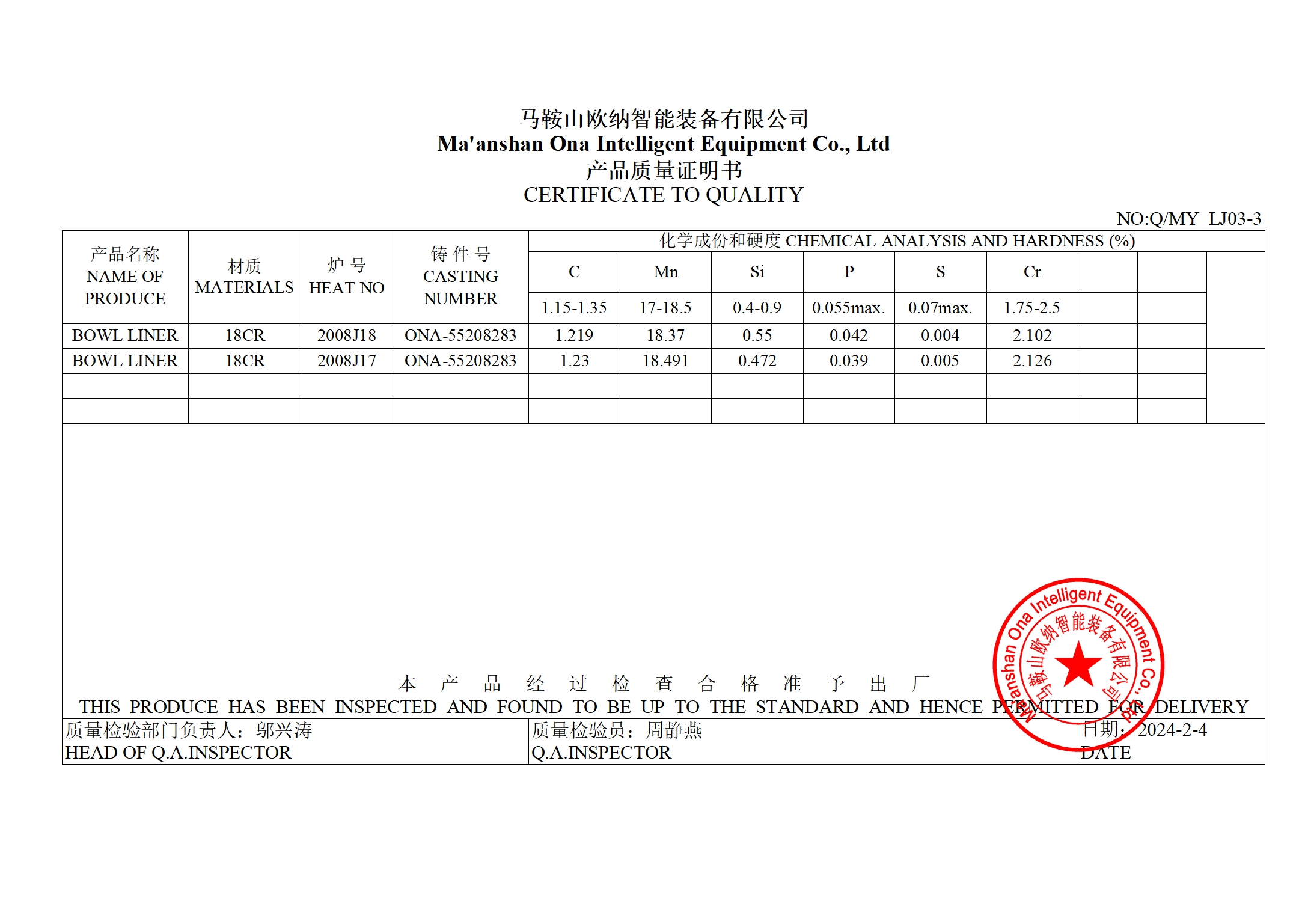
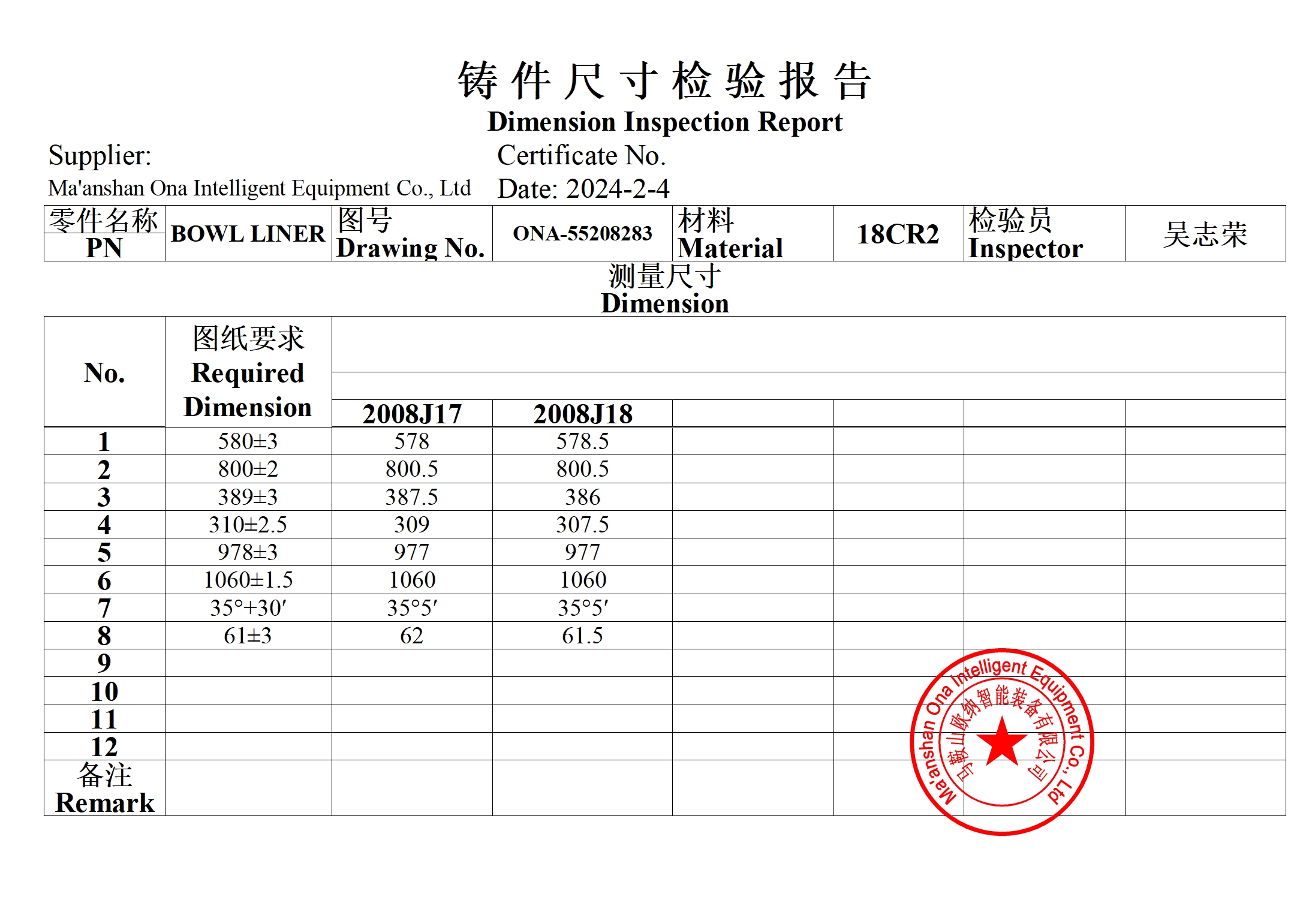
- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search

loading












C125
ONA
847490
Product Overview
Jaw plates' manufacturing process includes heat treatment as a critical step to enhance their wear resistance. The heat treatment process typically involves several key stages that are essential for improving the jaw plates' durability and performance:
1. **Quenching**: This is a rapid cooling process where the jaw plates are heated to a specific temperature above the material's critical point, and then quickly cooled, often in oil or water. This process forms martensite, a hard microstructure that significantly increases the hardness and wear resistance of the steel .
2. **Tempering**: After quenching, the jaw plates are tempered, which involves heating them to a lower temperature and then cooling them slowly. This process reduces the internal stresses induced by quenching and refines the martensitic structure, improving the toughness and durability of the jaw plates without significantly reducing their hardness .
3. **Microstructure Control**: The heat treatment process aims to control the microstructure of the steel. For example, the formation of a fine distribution of carbides within the martensitic matrix can further enhance wear resistance .
4. **Second Hardening**: Some high-alloy steels, like those used in ONA jaw plates, may undergo a secondary hardening process. At specific temperatures during the tempering process, the steel can achieve maximum hardness and wear resistance due to the precipitation of alloying elements like chromium and molybdenum .
5. **Surface Treatments**: In addition to bulk heat treatment, surface treatments like induction hardening or nitriding may be applied to further increase the surface hardness and resistance to abrasive wear .
6. **Optimization of Heat Treatment Parameters**: ONA likely uses simulation software to optimize the heat treatment parameters for their jaw plates, ensuring that the materials achieve the desired balance of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance .
The specific heat treatment process for jaw plates would be tailored to the alloy composition and the intended application of the crusher. The goal is to produce a jaw plate that can withstand the abrasive and impact forces encountered in crushing operations while maintaining its structural integrity and service life. By carefully controlling the heat treatment process, ONA ensures that their jaw plates meet these demanding requirements.
Production Site
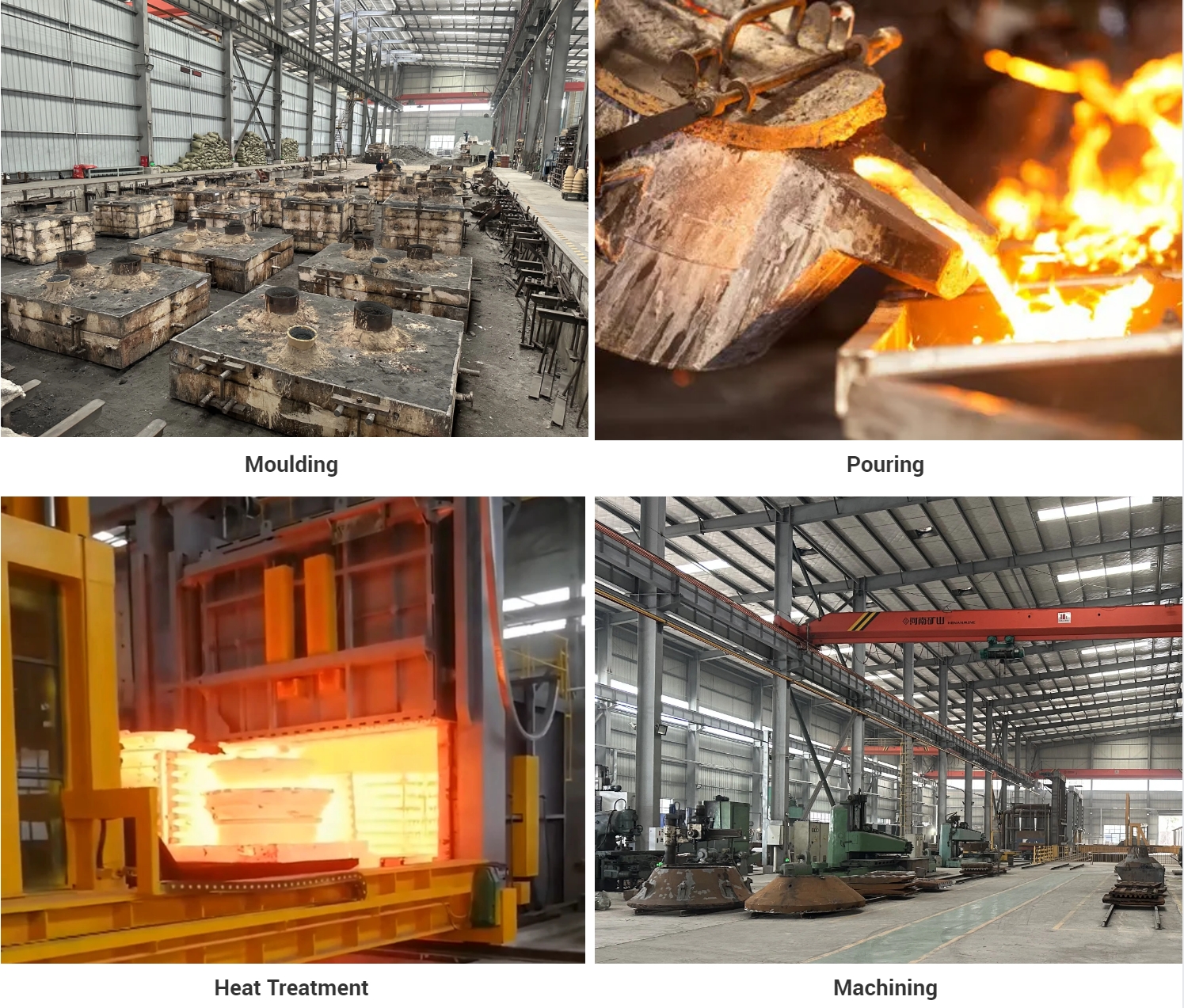

Our Advantages
Product Overview
Jaw plates' manufacturing process includes heat treatment as a critical step to enhance their wear resistance. The heat treatment process typically involves several key stages that are essential for improving the jaw plates' durability and performance:
1. **Quenching**: This is a rapid cooling process where the jaw plates are heated to a specific temperature above the material's critical point, and then quickly cooled, often in oil or water. This process forms martensite, a hard microstructure that significantly increases the hardness and wear resistance of the steel .
2. **Tempering**: After quenching, the jaw plates are tempered, which involves heating them to a lower temperature and then cooling them slowly. This process reduces the internal stresses induced by quenching and refines the martensitic structure, improving the toughness and durability of the jaw plates without significantly reducing their hardness .
3. **Microstructure Control**: The heat treatment process aims to control the microstructure of the steel. For example, the formation of a fine distribution of carbides within the martensitic matrix can further enhance wear resistance .
4. **Second Hardening**: Some high-alloy steels, like those used in ONA jaw plates, may undergo a secondary hardening process. At specific temperatures during the tempering process, the steel can achieve maximum hardness and wear resistance due to the precipitation of alloying elements like chromium and molybdenum .
5. **Surface Treatments**: In addition to bulk heat treatment, surface treatments like induction hardening or nitriding may be applied to further increase the surface hardness and resistance to abrasive wear .
6. **Optimization of Heat Treatment Parameters**: ONA likely uses simulation software to optimize the heat treatment parameters for their jaw plates, ensuring that the materials achieve the desired balance of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance .
The specific heat treatment process for jaw plates would be tailored to the alloy composition and the intended application of the crusher. The goal is to produce a jaw plate that can withstand the abrasive and impact forces encountered in crushing operations while maintaining its structural integrity and service life. By carefully controlling the heat treatment process, ONA ensures that their jaw plates meet these demanding requirements.
Production Site


Our Advantages

